What Are Compressive Neuropathies?
Compressive neuropathies occur when a nerve is pinched or compressed, often leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. These conditions can significantly impact daily life but are often treatable with timely intervention.
Common Types of Compressive Neuropathies
Compressive neuropathies can occur anywhere in the body. Here are some of the most common types:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
- Affects the median nerve at the wrist.
- Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, and weakness in the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
- Common in people with repetitive wrist movements or conditions like diabetes.
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
- Involves the ulnar nerve at the elbow.
- Symptoms: Pain and tingling in the ring and little fingers, often worsening with elbow bending.
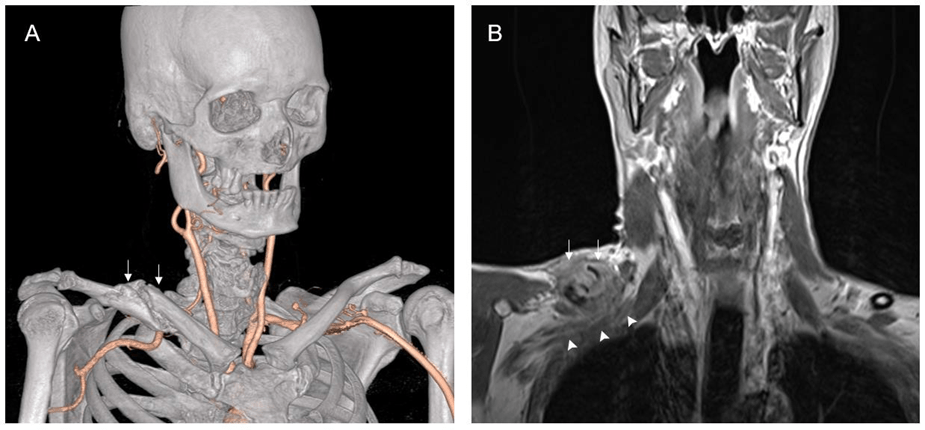
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)
- Compression of nerves or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet, located between the neck and shoulder.
- Symptoms: Shoulder and neck pain, numbness in the arm or hand, and sometimes vascular issues.
- Piriformis Syndrome
- Compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle in the buttock.
- Symptoms: Pain, tingling, or numbness in the buttock and down the leg.
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Affects the tibial nerve as it passes through the tarsal tunnel near the ankle.
- Symptoms: Burning pain, tingling, or numbness in the sole of the foot.
What Causes Compressive Neuropathies?
Several factors can lead to nerve compression:
- Repetitive Movements: Repeated motions or prolonged positions can strain nerves.
- Trauma or Injury: Fractures or dislocations can cause nerve compression.
- Inflammation: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or swelling from other causes.
- Anatomical Variations: Some people are predisposed due to unique anatomical structures.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of compressive neuropathy vary depending on the affected nerve but commonly include:
- Pain or aching in a specific area.
- Tingling or “pins and needles.”
- Numbness or loss of sensation.
- Weakness in the affected muscles.
If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation to prevent permanent damage.
How Are Compressive Neuropathies Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Assessing symptoms and performing nerve-specific tests.
- Electrodiagnostic Testing: EMG and nerve conduction studies to measure nerve electrical function.
- Imaging: MRI, ultrasound, or X-rays might be done to identify structural causes.

Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
- Non-Surgical Approaches
- Rest, activity modification, and ergonomic adjustments.
- Splints or braces to reduce strain.
- Physical therapy to strengthen surrounding muscles and improve posture.
- Medications for pain and inflammation.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce swelling and relieve symptoms.
- Nerve blocks for pain management.
- Surgical Intervention
- Indicated when conservative measures fail or if there is severe compression.
- Procedures may include releasing the compressed nerve or removing the source of pressure.

Preventing Compressive Neuropathies
While not all cases are preventable, these steps can help reduce the risk:
- Maintain proper posture during work and daily activities.
- Take regular breaks from repetitive tasks.
- Strengthen and stretch muscles through regular exercise.
- Use ergonomic tools and supports as needed.


When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent pain, tingling, or weakness, it’s crucial to consult a specialist. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and prevent further complications.
Contact Us
If you’re dealing with symptoms of compressive neuropathy, I’m here to help. Let’s work together to find the best treatment plan for you.
Disclaimer
This fact sheet is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment options.
The information provided here reflects general practices and may not apply to your individual health circumstances. Outcomes and risks may vary depending on your medical history, condition, and response to treatment.
If you experience any concerning symptoms or side effects following a procedure, contact your healthcare provider immediately or seek emergency medical attention.
This material is not intended to promote or endorse any specific treatment or procedure. Decisions about your healthcare should always be made in consultation with your physician, considering your unique health needs and goals.